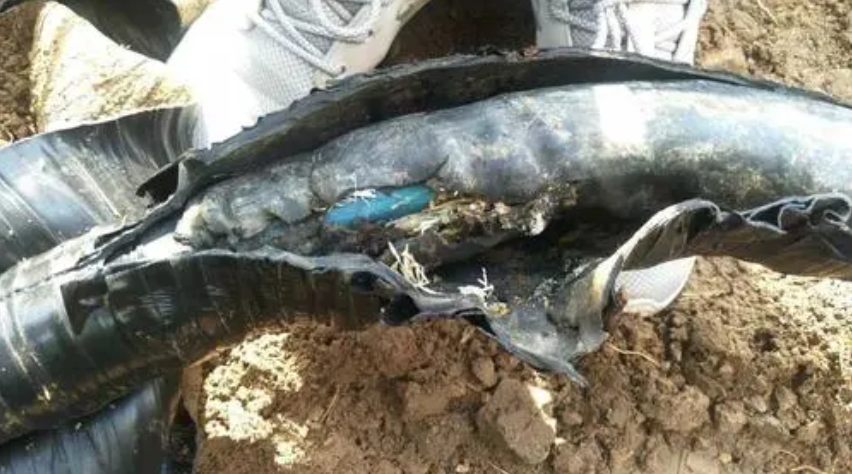
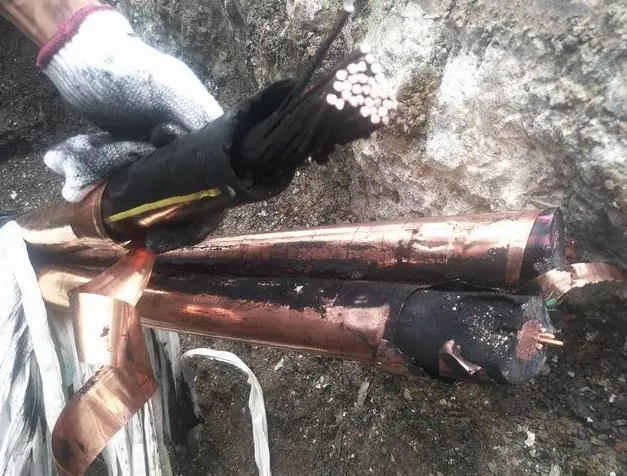
Cable troubleshooting is one of the common problems in power grid operation and maintenance, there are many kinds of cable faults including short circuit, circuit breakage, leakage, etc. These faults are likely to cause the cables to fail to operate normally, resulting in accidents such as interruption of power supply, damage to power equipment and even casualties, which will have a serious impact on the users and the power grid.
For cable faults, it is first necessary to carry out field investigations and observations to understand the specifics and possible causes of the fault, including checking the joints, insulation, metal sheaths and other parts of the cable and observing whether there is any damage, corrosion, aging and other phenomena. The location and nature of the fault can be determined qualitatively and quantitatively by testing and measuring with cable fault testing and location instruments. Commonly used testing methods include resistance testing, insulation testing, partial discharge testing, etc. By analyzing the test and measurement results and combining them with the field investigation and observation, the cause of the cable fault is judged and fault repair is carried out.
This cable fault location method mainly relies on manual inspection and measuring instruments, cumbersome steps, not only time-consuming and laborious and low positioning accuracy, unable to meet the needs of high-quality operation and maintenance of power grids. In order to improve the efficiency and accuracy of cable fault location, Shenzhen Dingxin Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd. has developed a high-voltage cable fault and hidden danger monitoring system, which can simultaneously collect 7 high-frequency signals, monitor the working status of cables in real time, locate the fault point, and warn of potential safety hazards.
High-voltage cable fault and hidden danger monitoring system DX-WPS100-GZ02 is installed in the cable joints using a distributed method, once the line fault, the system can quickly capture the fault traveling wave signal, wireless upload to the monitoring center, based on the topology of the topology of the distributed traveling wave algorithm to carry out a comprehensive analysis, can quickly locate the fault point, but also based on the capture of the traveling wave fault waveforms to determine the type of fault, and push the results to the mobile phone or through the WEB and other clients to view the details of the fault. The result is pushed to the cell phone or through the WEB, client, etc. to view the detailed information of the fault, monitoring the hidden current signals captured can also provide a basis for judgment to prevent the occurrence of faults, early warning of potential hazards, to prevent fault tripping.